
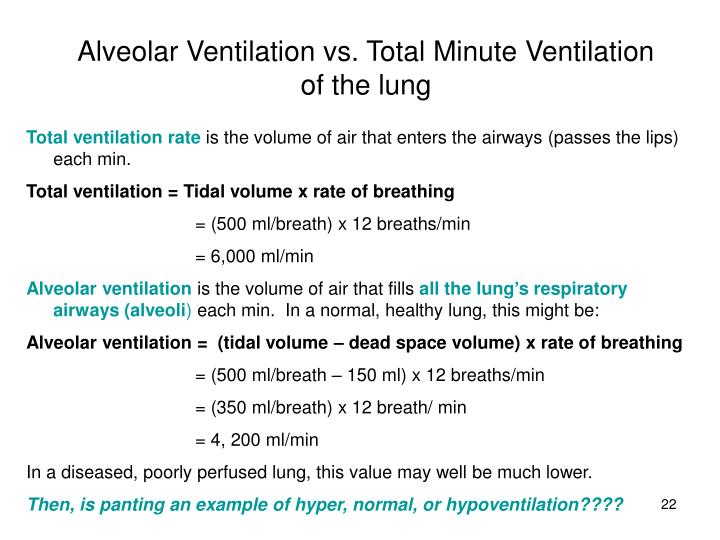
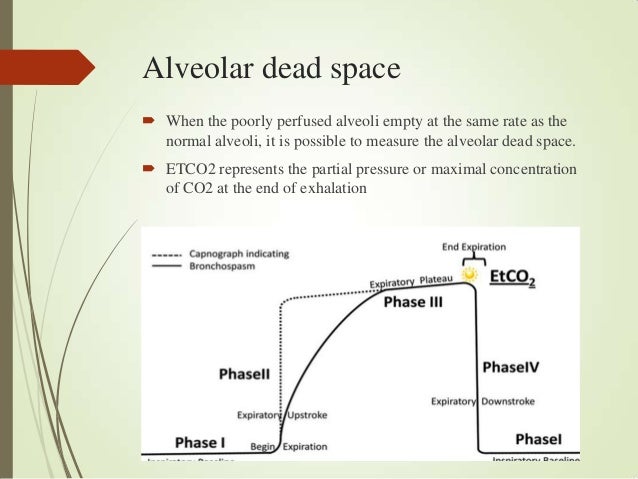
How do you calculate alveolar in dead space?Įstimating the dead space can be of significant value in clinical situations for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic value.What is a normal alveolar ventilation rate?.What is the average alveolar ventilation?.Why does positive pressure ventilation increase dead space?.What happens to dead space during exercise?.How does dead space affect alveolar ventilation?.Which best defines alveolar gas exchange?.What happens when alveolar dead space increases?.What is the difference between anatomical and alveolar dead space?.Which disease is the alveoli ventilated but not perfused?.Differences between measured and set VT and the dependence of this difference on GA require further investigation. A volume guarantee setting of 4-5 ml/kg in the Dräger Babylog® 8000 plus ventilator may be inappropriate as a universal target across the GA range of 23-32 weeks. Despite similar VT/kg and VA/kg across all studied infants, respiratory rate and AMV/kg increased with GA.ĬONCLUSIONS: VD,app rather than anatomical VD is the major factor influencing increased VD,MM/VT at a younger GA. This association was primarily influenced by the appliance dead space. VD,MM/VT was negatively associated with GA after adjusting for birth weight Z score (p < 0.001, R(2) = 0.26). Tidal breathing variables were analysed using multivariable linear regression. RESULTS: Valid measurements were obtained in 43/51 (87%) infants. Tidal breathing analysis was performed in ventilated very preterm infants (GA range 23-32 weeks) on day 1 of life. METHODS: This was a single-centre, prospective, observational, cohort study in a neonatal intensive care unit. OBJECTIVES: We aimed to calculate respiratory dead space (VD) from the molar mass (MM) signal of an ultrasonic flowmeter (VD,MM) in very preterm infants on volume-targeted ventilation (VT target, 4-5 ml/kg) and to study the association between gestational age (GA) and VD,MM-to-VT ratio (VD,MM/VT), alveolar tidal volume (VA) and alveolar minute volume (AMV).
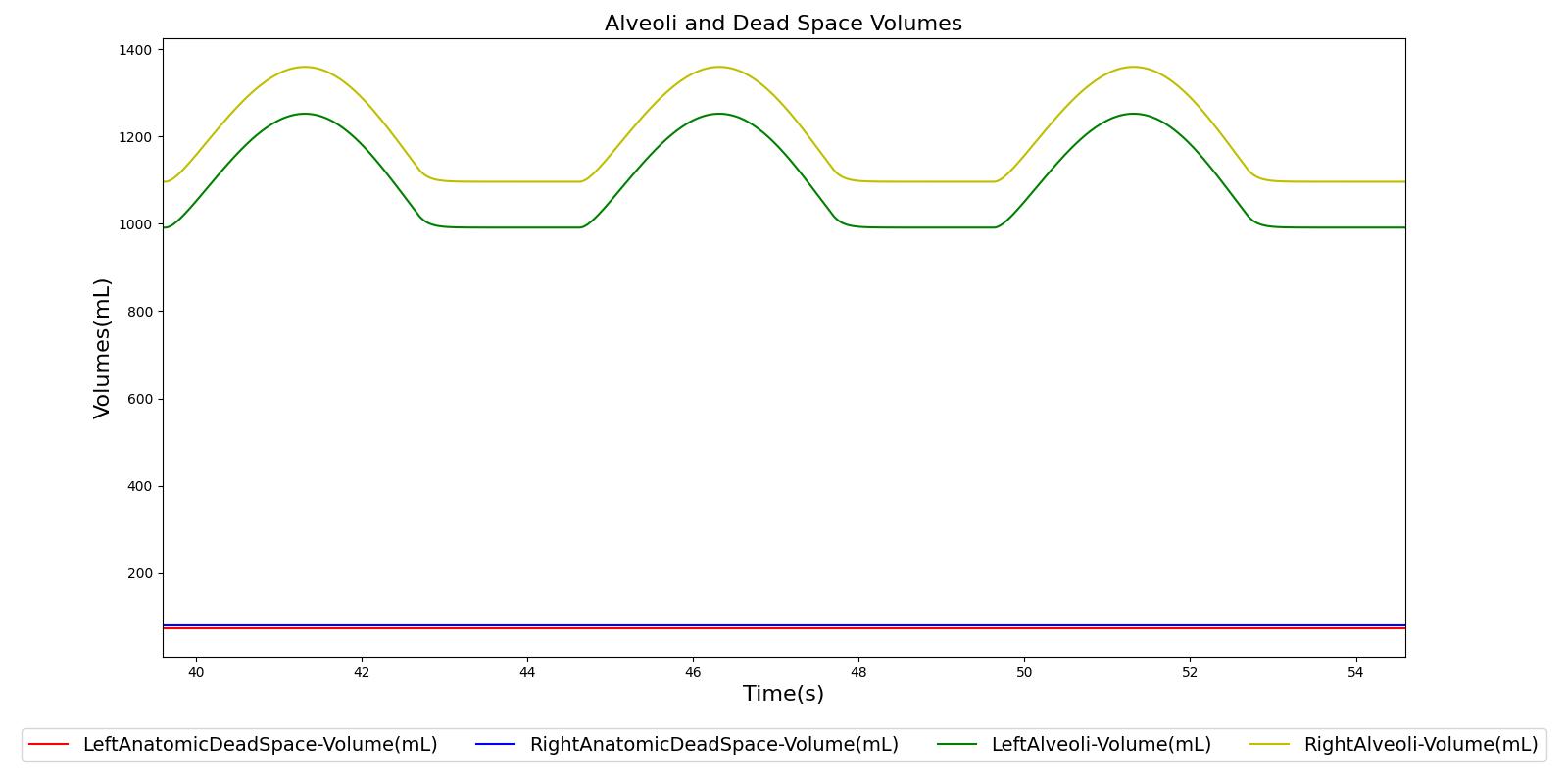
The optimal ventilator-delivered tidal volume (VT) in these infants is unknown and may depend on the extent of alveolarisation at birth. BACKGROUND: Ventilated preterm infant lungs are vulnerable to overdistension and underinflation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
